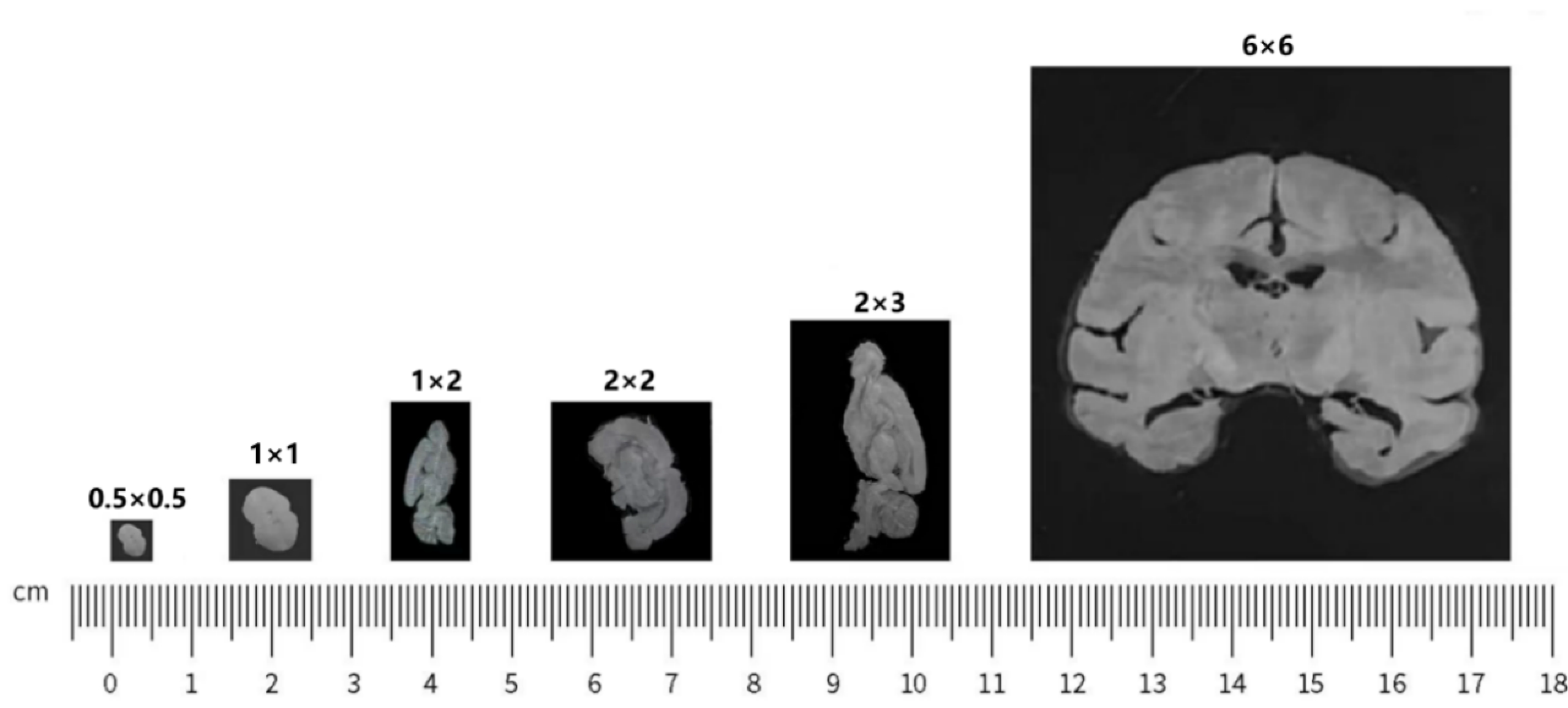
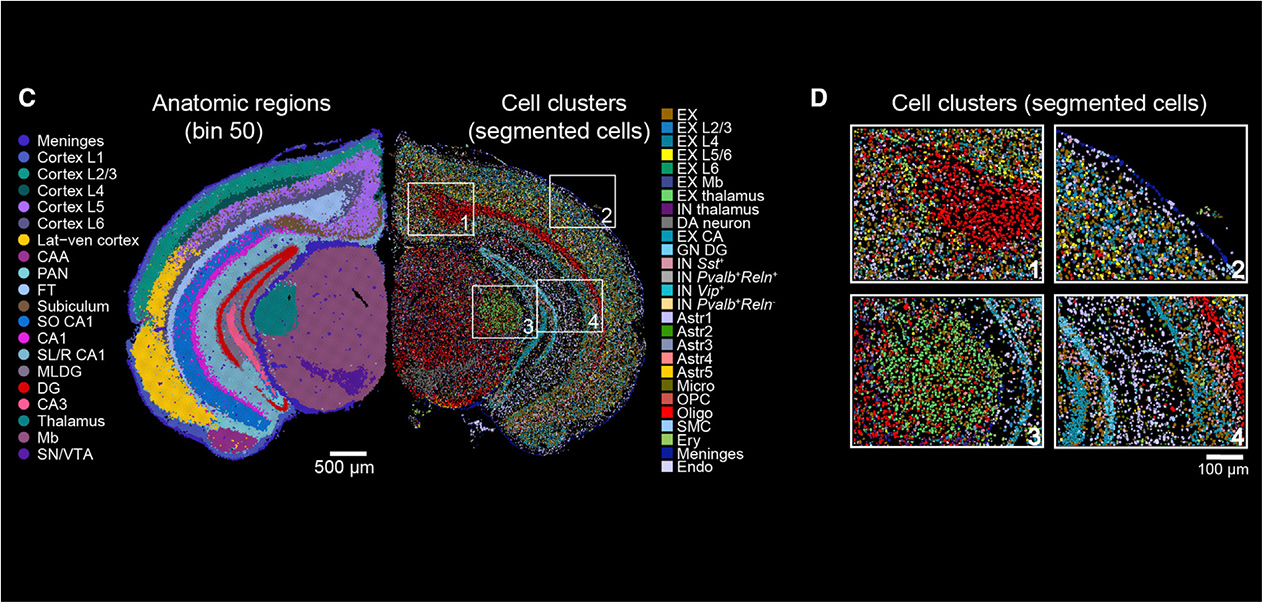
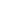Stereo seq is a spatiotemporal transcriptome technology independently developed by Huada, a leading domestic life science institution. This technology is based on DNA Nano Ball (DNB) and is an in situ panoramic technology with high throughput, ultra-high resolution, and large field of view. It can achieve simultaneous spatial transcriptome analysis of the same sample at four scales: organizational, cellular, subcellular, and molecular. This technology captures mRNA in tissues through spatiotemporal chips and restores it back to its spatial position through spatial barcodes (CID), achieving in situ sequencing of tissues. It establishes a strong research foundation for a deeper understanding of the relationship between gene expression, morphology, and local environment of cells.
Applications
Technical procedure

Sample preparation
Freeze and OCT embed the target tissue sample, then perform sectioning and RNA quality assessment. Section the OCT-embedded sample and then attach the sections to the surface of the chip.

Tissue permeabilization & library construction
Fix and permeabilize the tissue sections placed on the chip. The chip is equipped with a spatial capture probe that can bind to the mRNA molecules released by the tissue cells, thereby capturing the mRNA molecules in the target sample and synthesizing cDNA. Then, collect the cDNA and construct the sequencing library.

Sequencing
Use the ultra-high throughput DNBSEQ Tx series sequencers for sequencing.

Data analysis and visualization
Perform quality control on the sequencing data and complete the full analyses, ultimately obtain gene expression information of the tissue cells in their spatial locations.
STOmics ® Stereo seq Translucent Reagent Kit
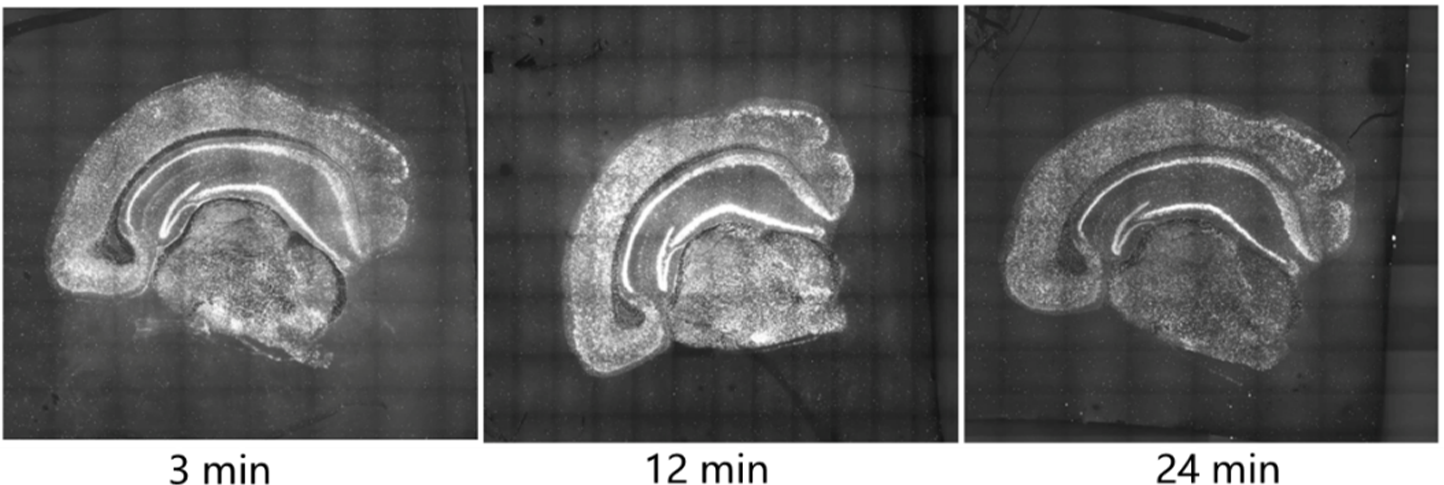
The STOmics® Stereo-seq clearing reagent kit is a pre-experiment reagent kit used to determine the optimal clearing time for tissue sections. The Stereo-seq Chip P (clearing test chip) contains nucleotide capture probes that bind to the tissue section. These probes capture mRNA molecules in situ within the tissue, followed by cDNA synthesis using fluorescently labeled nucleotides. Researchers can then quickly determine the optimal clearing time for specific tissues through fluorescence microscopy imaging. Choosing the optimal clearing conditions facilitates better mRNA capture. The best clearing time is determined by maintaining consistent imaging conditions (including brightness and exposure) and ensuring the tissue morphology is intact, the fluorescence signal is strongest, and there is no dispersion. When cleared for 3 minutes, the tissue exhibits uneven brightness in the same cortex, indicating insufficient clearing. At 12 minutes of clearing, the details are clear, the signal is uniform, and the brightness is maximal. At 24 minutes of clearing, the signal is weaker than that at 12 minutes. Therefore, the optimal clearing time is 12 minutes.
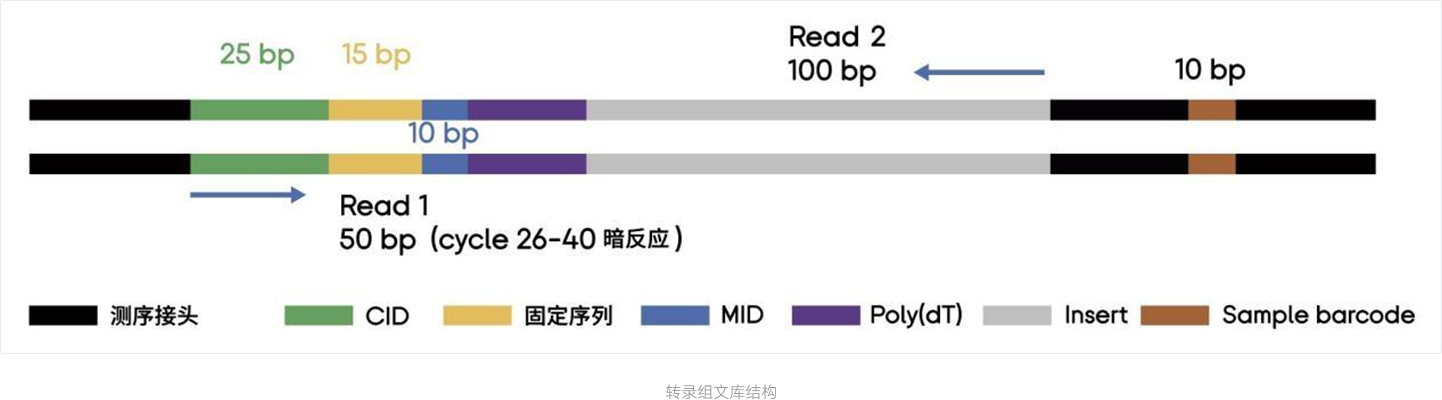
STOmics ® Stereo seq Transcriptome Kit
The STOmics® Stereo-seq transcriptome reagent kit is used to construct a 3' end full-transcript library from tissue sections. The Stereo-seq Chip T (spatiotemporal poly-T chip) contains capture probes with spatial coordinate information. These probes bind to the tissue section and capture mRNA molecules in situ, followed by cDNA synthesis. Researchers can obtain ultra-high resolution spatial transcriptome information of specific samples through DNBSEQ sequencing and the complementary STOmics® visualization analysis tools.
By using the Stereo-seq library construction kit, you can generate a Stereo-seq sequencing library. This efficient biochemical workflow, combined with powerful visualization analysis tools, enables ultra-high resolution spatial omics.

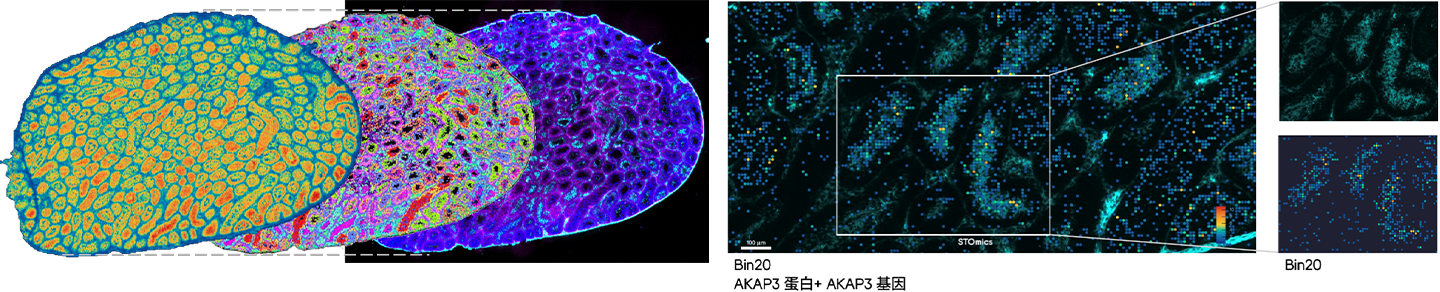
Technical Procedure—Simultaneous Detection of Ultra-high Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics and Proteomics
Bioinformatics analysis tools
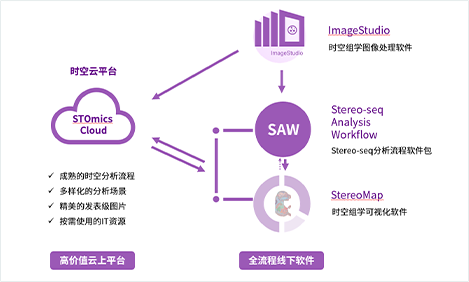
The Stereo-seq technology offers users various data analysis solutions. In addition to the STOmics Cloud solution, which allows for cloud-based data analysis and visualization through user-submitted sequencing data and image files, there is also the offline ImageStudio+SAW+StereoMap combination solution. This solution enables image processing, data analysis, visualization, and result adjustment on the chip.