Plant & Animal whole-genome sequencing refers to the DNA sequencing of a species with known genome sequences, and then complete individual or group analysis. Through sequence alignment, a large amount of Variation information can be detected, including SNP, Insertion/Deletion sites, Structure Variation sites, Copy Number Variation sites, etc., thus, to obtain the genetic variation map of different individuals of the same species. Using whole genome sequencing technology can help quickly identify genetic variations related to the important traits of animals and plants, which can be used in molecular breeding to shorten breeding time.

Rolling circle amplification constructs DNB sequencing library, PCR-free resequencing detects InDels more accurately. No worries about index hopping. Low duplication rate without manual intervention.
DNBSEQ-T20 has ultra-high throughput, short cycles, and high cost-effectiveness.
Applications

Target Trait Gene Mining
Group Genetics Research

Variation Graph Construction
Molecular Markers Development and Marker-Assisted Selection Breeding

Species/Variety Identificaition
Census of Core Animal and Plant
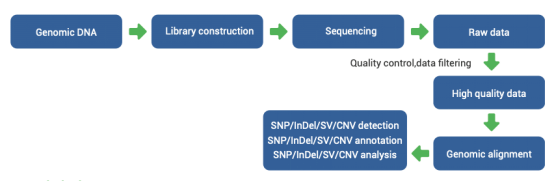
Technical procedure
Technical parameters

Sample requirements
Genomic DNA, no degradation or slight degradation.

Sample requirement (single time)
≥ 1ug

Sample concentration
≥ 12.5ng/uL

Recommended data volume
Individual resequencing is recommended to be more than 30X, group resequencing is recommended to be more than 10 X.