3K Rice Sequencing & Pan-genome Research
Research background
The 3,010 rice samples (from 89 countries and regions around the world) represent about 95% of the core germplasm diversity of 780,000 rice species worldwide. By whole genome resequencing, with an average sequencing depth of 14X per sample, a total of 32Mb of high-quality SNPs and InDels were detected using the resequencing data. The structure and differentiation of cultivated rice populations in Asia were described in a more detailed and accurate way. The traditional 5 populations were increased to 9, namely, indica rice populations in East Asia (China), indica rice in South Asia, indica rice in Southeast Asia and modern indica rice varieties. Three japonica rice populations, namely temperate japonica rice, tropical japonica rice and subtropical japonica rice in Southeast Asia, as well as Aus and fragrant rice from India and Bangladesh.
This study reveals for the first time a large number of microstructural (> 100bp) variations (SVs, including translocations, deletions, inversions, and duplicates) among cultivated rice cultivars in Asia. The SVs of 453 strains with sequencing depth > 20X were studied. The phylogenetic tree constructed by SVs is similar to that of SNPS. A large number of SVs may be the genetic basis of different degrees of hybrid sterility and hybrid decay of XI and GJ. The pan-genome of Asian cultivated rice was constructed, including 12,770 (62.1%) core gene families and 9,050 (37.9%) distributed gene families. 12,000 new full-length genes and thousands of incomplete ones were discovered. The core genes are ancient, and most of the new genes appear younger and shorter in length.
Research Strategy
Initially, 3,024 rice samples were sequenced, 14 samples were filtered out for quality control, and 3,010 rice samples were retained for research. The 3K RG sequencing data alignment to the reference genome Nipponbare for detection of SNPs and InDels. The pan-genome was constructed by the Nipponbare genome sequence and the newly assembled genome sequence without redundancy. Perform SVs and PAVs analysis on 453 rice materials with sequencing depth > 20X and alignment depth > 15X.
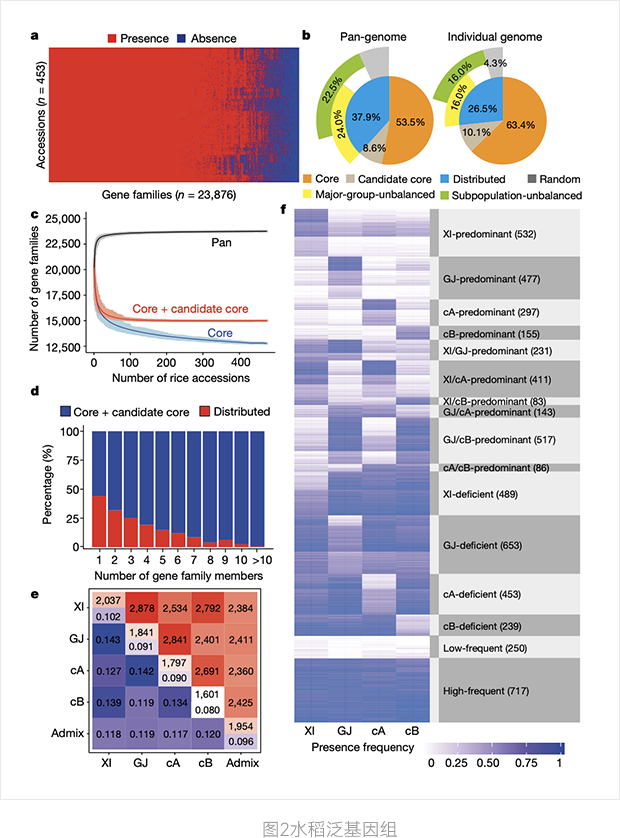
a. PAVs gene family
b. The components of a pan-genome and a separate genome
c. Simulated pan-genome and core genome based on 500 randomly selected rice genomes
d. Proportion of core and distributed gene families
e. Average difference in the number of gene families between two strains
f. 5733 Main group unbalanced gene family characteristics
References
Wang W, Mauleon R, Hu Z, et al. Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice[J]. Nature, 2018,557(7703): 43.