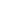Research methods
01 Technical Principles
DNBelab C4 technology is a droplet microfluidics system based on negative pressure. By introducing the droplet tagging technology (Disc-seq: Droplet-indexed high-throughput single-cell sequencing), it encapsulates labeled capture beads with individual cells or cell nuclei within droplets. Using the Droplet index technology, it achieves a super-Poisson distribution of beads. Within the droplets, cell lysis and the capture of mRNA or DNA molecular are performed, and the tag sequences from the beads within the same droplet are identified. Library construction and sequencing of cDNA and Droplet index can then be performed to obtain gene expression or chromatin accessibility information from a large number of cells in a single run. Compared to conventional droplet single-cell sequencing technologies, such as the Drop-seq platform, which has a cell recovery rate of 1%-3%, this technology increases the recovery rate to 30%-60%. This significantly improves cell utilization and reduces the number of cells required for each run.
02 Technical Procedure
The general workflow of single-cell sequencing includes steps such as cell suspension preparation, single-cell isolation, lysis, amplification, library construction, sequencing, and data analysis.

scRNA-seq
This technology uses a portable negative pressure device to encapsulate tagged mRNA capture beads with individual cells or cell nuclei in droplets. By employing the Droplet index technology, it achieves a super-Poisson distribution of beads. Within the droplets, cell lysis and mRNA molecular capture are performed, and the tag sequences from the beads within the same droplet are identified. Library construction and sequencing of cDNA and Droplet index can then be performed to obtain gene expression information from a large number of cells in a single run.
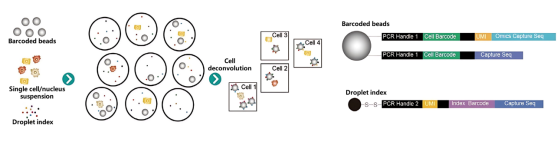
Figure 1: scRNA sequencing technology based on the DisC-seq
scATAC-seq
Single-cell ATAC-seq involves enriching cell nuclei from tissues or cells, then using Tn5 transposase to cut chromatin accessibility regions. Using the DNBelab C4 single-cell device, the transposed cell nuclei and tagged beads are encapsulated. Within the droplets, chromatin accessibility regions are enriched and amplified. Subsequently, libraries can be prepared and sequenced following high-throughput sequencing workflows, and bioinformatics analysis can be performed. The transposed cell nuclei are loaded onto the chip in a range of 5,000-15,000, resulting in data from 1,500-9,000 cells, with a doublet rate of less than 5%.

03 Library Construction Procedures
scRNA-seq
1) Reverse transcription: After demulsification of the generated droplets, construct the reverse transcription reaction system to complete RNA reverse transcription.
2) Second-strand synthesis: Use the second-strand synthesis reaction system to synthesize the second strand from the reverse transcription product.
3) PCR amplification: Perform PCR amplification on the synthesized cDNA according to the set PCR reaction system and parameters.
4) Purification of cDNA and oligo products: Purify the PCR products using Cleanup Beads A to separately purify the cDNA and oligo products.
5) Library quality test: Use 1μl of cDNA and oligo products to measure concentration with the Qubit dsDNA HS Kit, and use the Agilent DNA Analysis Kit to check fragment distribution.
6) Sequencing: Once the library passes quality checks, proceed with sequencing.
scATAC-seq
1) Enzyme treatment: After demulsification of the generated droplets, perform enzyme treatment using the ATAC Enzyme II reaction system to remove redundant fragments.
2) PCR amplification: Perform PCR amplification on the recovered DNA according to the set PCR reaction system and parameters.
3) Purification of PCR amplification products: Purify the PCR products using Cleanup Beads A.
4) Library quality test: Measure the concentration of the DNA product using the Qubit dsDNA HS Kit, and check the fragment distribution using the 2100 High Sensitivity Chip.
5) Library QC passed, proceed to sequencing
04 Sequencing Strategy
Sequencing with the DNBSEQ Tx series ultra-high-throughput sequencer.
scRNA-seq
Sequencing read length: 30+100+10bp Sequencing data volume: 500M reads
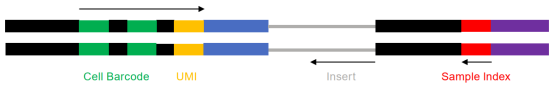
Figure 2: Schematic of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) Strategy.
scATAC-seq
Sequencing read length: 20+50+50bp Sequencing data volume:500M reads
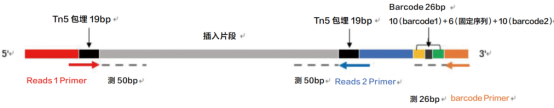
Figure 3 scATAC sequencing Strategy.
05 Data Analysis
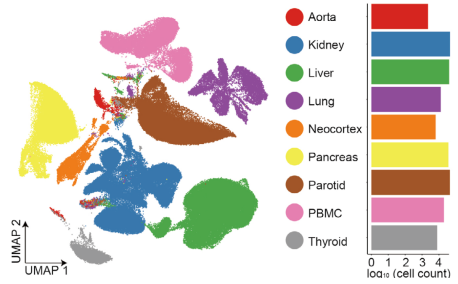
Figure 4 UMAP clustering results at the tissue/organ level for rhesus monkey single cells (left) and the number of cells in each tissue passing quality control (right).
Figure 5 Cell type annotation for all Clusters in the crab-eating macaque (Left) and the number of cells of each cell type passing quality control(Right).
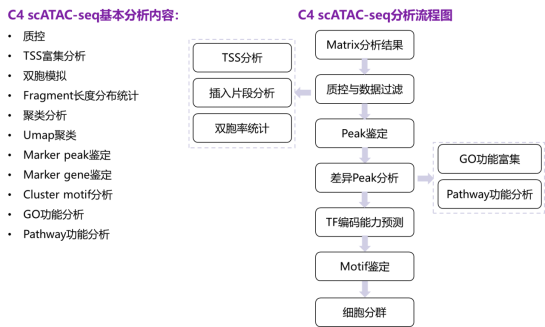
Figure 6 C4 scATAC-seq analysis workflow
C4 scATAC-Seq results display:
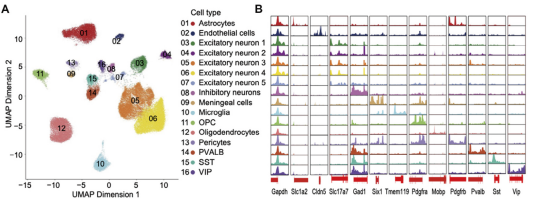
Figure 7A: UMAP clustering plot of SCATAC-Seq data from rat cerebral cortex samples (a total of 29,023 single cell nuclei data).
Figure 12B: Chromatin accessibility regions of marker genes and housekeeping genes in different cell types (e.g., the TSS region of the Tmem119 gene is only detected in microglia and not in other cell types).